Patterns in the Periodic Table
1 Complete the sentences and diagram below.
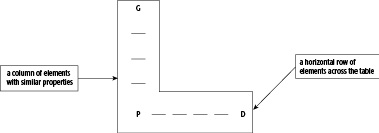
Scientists look for patterns in data. Historically, when they arranged the known elements in order
of relative ……………..……………………………, they found that there was a repeating pattern.
Thesepatterns were shown clearly when the elements were arranged in a ……………..…………
Each row in the table is called a period, with metals on the ……………..………………………
and ……………..……………………… on the right. The vertical columns of elements in the tablewere made up of elements with ……………..…………………………… properties.
Modern versions of the Periodic Table put the elements in order of ……………..…………… number,also known as the atomic number.
The Periodic Table of the elements
Part 1
Below are listed 36 elements with their chemical symbols and atomic weights (now referred to as relative atomic masses, Ar).
When chemists first arranged elements in a Periodic Table, they put them in order of their atomic weight starting on the left and filling each row in turn.
2 You should try to do the same. There are 36 spaces for the 36 elements in the grid provided. Write the symbol of the element and its atomic weight in sequence into the boxes in pencil.
|
Aluminium Al 27 |
Argon Ar 40 |
Arsenic As 75 |
Beryllium Be 9 |
|
Boron B 11 |
Bromine Br 80 |
Calcium Ca 40 |
Carbon C 12 |
|
Chlorine Cl 35.5 |
Chromium Cr 52 |
Cobalt Co 59 |
Copper Cu 63.5 |
|
Fluorine F 19 |
Gallium Ga 70 |
Germanium Ge 73 |
Helium He 4 |
|
Hydrogen H 1 |
Iron Fe 56 |
Krypton Kr 84 |
Lithium Li 7 |
|
Magnesium Mg 24 |
Manganese Mn 55 |
Neon Ne 20 |
Nickel Ni 59 |
|
Nitrogen N 14 |
Oxygen O 16 |
Phosphorus P 31 |
Potassium K 39 |
|
Scandium Sc 45 |
Selenium Se 79 |
Silicon Si 28 |
Sodium Na 23 |
|
Sulfur S 32 |
Titanium Ti 48 |
Vanadium V 51 |
Zinc Zn 65 |
Now look at a modern Periodic Table. Have you made any mistakes? Correct them and go over your work in ink.
Draw in a line dividing the metals from the non-metals.
3. Consider the position of hydrogen in the table. Give one reason why it could be placed in Group I, as this table suggests, and one reason why not.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The Periodic Table
Below are the first 36 elements in the periodic table with their atomic numbers, as seen in Part 1.
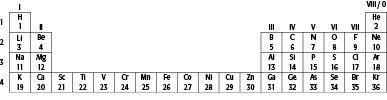
4. Give the symbol for one example of each of the following:
a a metal
b a gas
c a transition element
5. Find Cl (chlorine) in the table above.
a What is the group number?
b Which period is it in?
c How many electron shells does it have?
d How many electrons are there in its outer shell?
6. Explain what is meant by ‘atomic number’.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
7. a What name is given to the elements in Group VIII / 0?
b When Mendeleev was drawing up his first suggestions for the Periodic Table, the elements in Group 0 had not yet been discovered. Suggest a reason for this.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Noble and inert!
The boxes below represent the particles of different gases. One box shows the particles of elements in Group VIII / 0.
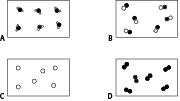
8. a What name is given to Group VIII / 0 (8) elements? ………………………………………..
b Name twoelements from Group VIII / 0. ………………………………………..
9. a Which box best represents particles from Group 0 elements? ………………………………………..
b Explain the reason for your answer.
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
10. A lighted splint is put into a gas jar of helium. What would happen?
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………………
11. Some properties of elements change as you go down their group in the periodic table. Research the library or the internet and, for each property listed below, comment on whether it changes as you go down Group VIII / 0 and, if so, how it changes.
a Reactivity:
……………………………………………….………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
b Density:
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
12. Which would be the best method to distinguish between different samples of Group VIII / 0 gases? Choose from the list below:
i Shake the sample with water and add an indicator.
ii Carry out a flame test.
iii Put a lighted splint into a sample of each gas.
iv Measure the density of each.
Properties of the noble gases
Tilly has filled balloons with three different gases. The symbols for the gases are written on the balloons. The diagram shows what happens if she then simply holds the balloons by their string.
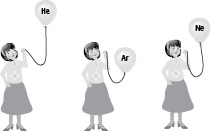
13. To which group of the Periodic Table do the gases belong?
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………………
14. a Predict what would happen to a balloon filled with krypton.
……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
b Explain the reason for your answer.
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
……………………………………………….………………………………………………………
15 . Helium is often used to fill weather balloons and airships. Give tworeasons why this is a good choice.
……………………………………………….………………………………………………………………
16. Neon, argon and krypton are used to fill light bulbs. Give a reason for this.
……………………………………………….………………………………………………………………
The third period
The table shows the elements in the third period of the Periodic Table. Samples of each of the elements were burnt in oxygen and the oxides formed were tested to see whether they were acids or bases.

17. a How many electron shells does the third period have? ……………………………….
18. a Which three elements in the third period are metals?
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
b What trends do you notice about metallic properties as you go across the period?
……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
19. a Oxygen is in Group VI. What does this tell you about the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom of oxygen?
……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
The Periodic Table: the halogens
Sarah is diving into a swimming pool. She can smell chlorine.

20. a Explain why there is chlorine in the swimming pool.
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
b Iodine is in the same group of the Periodic Table as chlorine. Give a use of iodine.
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
21. Chlorine and iodine are in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
a What name is given to Group VII elements? ……………………………
b Is chlorine a metal or a non-metal? ……………………………
c Is iodine a metal or a non-metal? ……………………………
d Name a type of organic life that is a source of iodine? ……………………………
22. a The atomic number of chlorine is 17. What key information does this tell you about chlorine?
……………………………………………….…………………………………………………………
b i What is the electron arrangement of chlorine? ……………………………
ii How many electron shells does it have? ……………………………
iii What period is it in? ……………………………
c) Iodine has five electron shells. How many electrons are in the outer shell of iodine?
……………………………………………….………………………………………………………
23. The symbol for chlorine is Cl iodine is I and sodium Na.
Chlorine combines with sodium to make sodium chloride, NaCl
Iodine also reacts with sodium.
What will be the name and formula of the compound formed?……………………………………………….……………………………………………………………
Topic: The Periodic Table
Trends in Group 7 – The Halogens
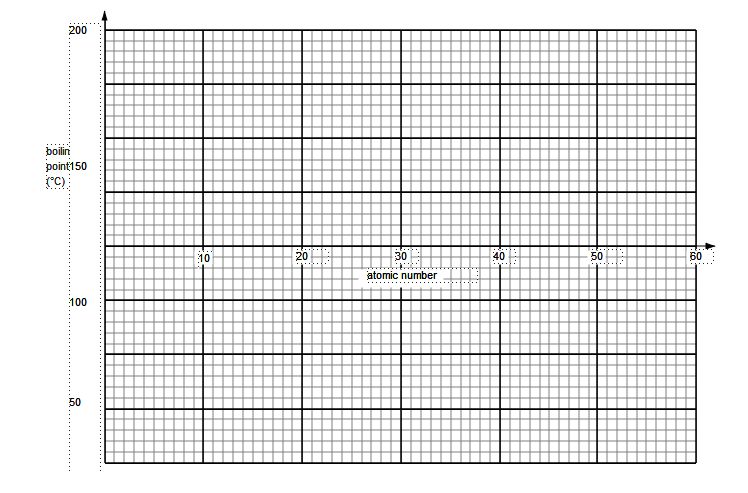
Look at the table below:
|
halogen |
atomic number |
boiling point (°C) |
|
fluorine |
9 |
–188 |
|
chlorine |
17 |
–34 |
|
bromine |
35 |
58 |
|
iodine |
53 |
184 |
Plot this information on the graph below:
Questions
24. a). What is the pattern going down Group 7?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
b) . Which halogens are gases at room temperature (25 °C)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
c) . Astatine is below iodine in Group 7.
Predict its physical state at room temperature. _____________________
Trends in group 1 – The alkali metals
Look at the table below:
|
Element |
Atomic number |
Melting point (oC) |
|
Lithium |
3 |
180 |
|
Sodium |
11 |
98 |
|
Potassium |
19 |
63 |
|
Rubidium |
37 |
39 |
|
Casesium |
55 |
29 |
Questions
25. i. (a) . How does the melting point change as you go down Group 1?
________________________________________________________________
b). What state are these elements likely to exist in at room temperature?
__________________________________________________________________
c). How does the size of the atom change as you go down a group?
__________________________________________________________________
d). Describe how the size of the atom changes with the melting point.
__________________________________________________________________
ii) . Francium is below Caesium in the periodic table. Suggest what the melting point may be?
What state do you predict francium to be in at room temperature? __________________________________________________________________
Mid-table elements
Below is the upper part of the Periodic Table, giving the elements with their atomic numbers.
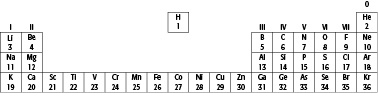
26. a What is the name given to the row of elements between atomic numbers 21 and 30 in the table?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…...
b Are they metals or non-metals?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…...
c What do the following symbols stand for?
Fe: …………………..…...Cu: …………………..…...
Zn: …………………..…...Mn: …………………..…...
V: …………………..…...
27. Below are some properties of two elements.
|
Element |
Melting point/°C |
Boiling point/°C |
Relative density /g/cm3 |
|
A |
1535 |
2750 |
7.87 |
|
B |
97.5 |
892 |
0.97 |
a) Which element is from the group of elements between atomic numbers 21 and 30?
…………………………………….……………………………………………………………………….
b) Which group in the Periodic Table do you think element A is in? …………………………..…...
c) Using information from the properties in the table as a guide, suggest whether elements similar to A or B would be more suitable for making a kettle. Give reasons for your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…...
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…...
d) )Element number 22 is called titanium. From its position in the Periodic Table predict threeproperties you would expect it to have. Put a tick in the box by one property from each pair in the list below.